New Delhi: India’s economy has emerged as a rare island of stability in a period of heightened global economic turbulence, supported by a calibrated fiscal strategy, disciplined consolidation, and resilient revenue mobilisation, the Economic Survey 2025–26 said. The Survey was tabled in Parliament today by Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman.
The Survey underlined that a predictable and credible fiscal trajectory adopted by the Centre over recent years has anchored macroeconomic stability while balancing growth imperatives with fiscal sustainability. Reduction in fiscal and revenue deficits, reorientation of spending towards capital expenditure, and stronger Centre–State coordination have collectively strengthened India’s macroeconomic framework and investor confidence.

Fiscal Prudence and Consolidation
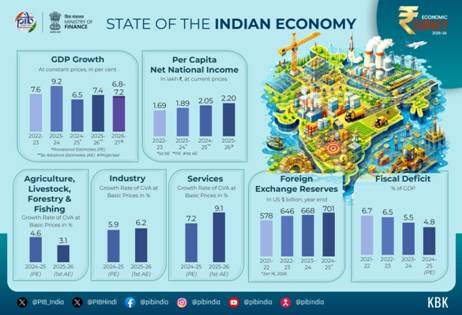
According to the Survey, the fiscal deficit is budgeted at 4.4 per cent of GDP in FY26, down from 4.8 per cent in FY25. The revenue deficit has been brought down to 0.8 per cent of GDP in FY26—the lowest since FY09—signalling a marked improvement in the quality of expenditure and leaving greater fiscal space for capital creation.
Revenue expenditure moderated from 13.6 per cent of GDP in FY22 to 10.9 per cent in FY25, while expenditure on major subsidies was rationalised from 1.9 per cent of GDP in FY22 to 1.1 per cent in FY26, even as food security coverage for nearly 78.9 crore beneficiaries was maintained.
Stronger Revenue Mobilisation
The Survey highlighted sustained improvement in revenue mobilisation, driven by better compliance and technology-led reforms. Revenue receipts rose to 11.6 per cent of GDP in FY25, aided by improved collection efficiency and curbing of leakages. Income tax return filings increased sharply from 6.9 crore in FY22 to 9.2 crore in FY25, reflecting a widening tax base and rising formalisation.
The share of direct taxes in total tax revenue increased to 58.2 per cent in FY25 from 51.9 per cent in the pre-COVID period. Gross GST collections during April–December FY26 stood at ₹17.4 lakh crore, compared with ₹16.3 lakh crore in the same period last year, supported by a steady expansion of the GST taxpayer base to over 1.5 crore.
The Survey noted that the proposed transition towards GST 2.0, including a simplified rate structure, is expected to reduce compliance costs, enhance trade competitiveness, incentivise formalisation, and support domestic manufacturing and consumption.

Capital Expenditure and Centre–State Partnership
A key pillar of fiscal strategy has been sustained capital expenditure. Effective capital expenditure increased from an average of 2.7 per cent of GDP in the pre-pandemic period to 4.3 per cent in FY26. Infrastructure sectors such as roads, railways, aviation, waterways, telecom, housing, and urban development accounted for a significant share of this spending.
The Special Assistance to States for Capital Expenditure (SASCI) scheme has played a critical role in sustaining State-level capex at around 2.4 per cent of GDP. Over the last five years, the Centre has allocated ₹4.5 lakh crore to States through interest-free loans, enabling long-term asset creation while balancing reform-linked and State-priority investments.
Debt Sustainability and Outlook
India’s debt-to-GDP ratio declined to 55.7 per cent in FY25, down by 7.1 percentage points since 2020, and remains on track to reach around 50 per cent by FY31. The Survey noted that India’s public investment efficiency stands out among peer economies, with general government investment at about 4 per cent of GDP.
Looking ahead, the Economic Survey emphasised the need for continued fiscal discipline, especially at the State level, alongside reforms to reduce cross-subsidies, enhance equity monetisation, improve expenditure efficiency, and deepen tax reforms including GST 2.0 and personal income tax simplification.
Overall, the Survey concluded that India’s calibrated fiscal strategy, underpinned by sustained capital expenditure, resilient revenues, and prudent debt management, has provided a strong anchor of stability and confidence amid an uncertain global economic environment.